프로그램은 자신이 직접 짠 코드에 여러 라이브러리를 섞어서 만든다.
섞는 방식은 두 가지가 있다.
하나는 정적 라이브러리로 만드는 것이고, 다른 하나는 동적 라이브러리로 만드는 것이다.
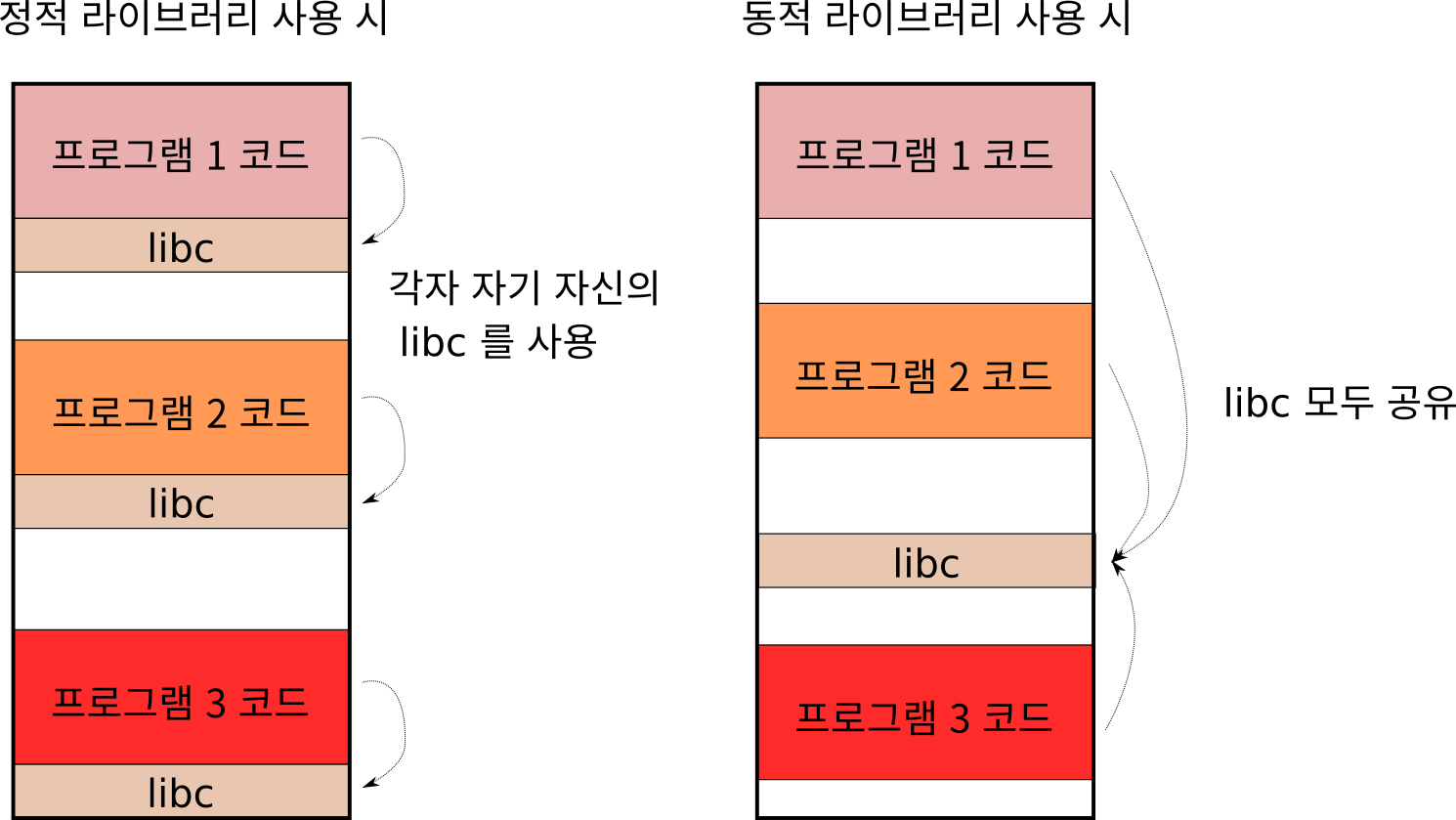 위의 그림이 두 라이브러리의 차이를 잘 보여준다.
위의 그림이 두 라이브러리의 차이를 잘 보여준다.
라이브러리가 다른 프로그램에서 많이 사용 된다면 동적 라이브러리로 만드는 것이 좋다.
하지만 동적라이브러리를 사용하면, 처음 시작할 때 해당 라이브러리의 위치를 파악하는데 오래 걸린다.
그래서 포토샵 같은 프로그램은 시작 할 때 오래 걸린다.
본 포스팅에서는 예제를 통해 static library와 shared library를 만들 것이다.
예제 코드 : https://github.com/luckydipper/c_cpp_compile_process/tree/main/make_library
시작하기 앞서, library를 만들 때 이름에 주의 해야한다.
파일 이름은 lib{name}.a 또는 lib{name}.so로로 하면 좋다.
clang과 gcc에서 -l flag로 library를 linking 할 때에는 파일 이름 앞에 lib이 적혀있어야 하기 때문이다.
또한 lib가 앞에 붙은 so 파일은 링크 시간에 사용되는 library로 설계한다.
만약 앞 부분에 lib가 없는 so 파일일 경우 runtime에 plug in 되는 library이다.
목차
1.정적 라이브러리
2.동적 라이브러리
3. 출처
정적 라이브러리 $($static library$)$
링킹 할 때, 해당 라이브러리 전체를 실행 파일에 링킹한다.
정적 라이브러리 만드는 방법
예제 파일 구조
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| make_library/
├── Makefile
├── add.cpp
├── add.hpp
├── add.o
├── cube.o
├── div.cpp
├── div.hpp
├── div.o
├── mul.cpp
├── mul.hpp
├── mul.o
├── sub.cpp
├── sub.hpp
└── sub.o
결과 파일 arithmetic_operation.a
|
static Makefile
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| CC = clang++-9
flag = -c
add.o : add.cpp add.hpp
$(CC) $(flag) add.cpp
mul.o : mul.cpp mul.hpp
$(CC) $(flag) mul.cpp
sub.o : sub.cpp sub.hpp
$(CC) $(flag) sub.cpp
div.o : div.cpp div.hpp
$(CC) $(flag) div.cpp
arithmetic_operation.a : add.o mul.o sub.o div.o
ar r arithmetic_operation.a add.o mul.o sub.o div.o
|
ar의 r flag는 replace existing or insert new files into the archive
사칙 연산 파일 예시
1
2
| //add.hpp
int add(int a, int b);
|
1
2
3
4
| //add.cpp
int add(int a, int b){
return a + b;
}
|
정적 라이브러리 살펴보는 방법
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| ar -tv make_library/arithmetic_operation.a
//결과
rw-r--r-- 0/0 960 Jan 1 00:00 1970 add.o
rw-r--r-- 0/0 960 Jan 1 00:00 1970 mul.o
rw-r--r-- 0/0 960 Jan 1 00:00 1970 sub.o
rw-r--r-- 0/0 960 Jan 1 00:00 1970 div.o
|
정적 라이브러리 링킹하여 사용하기
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| make_library/
├── main.cpp
├── cube.cpp
├── cube.hpp
└── arithmetic_operation.a
// 실행 명령어
clang++-9 make_library/main.cpp make_library/cube.cpp make_library/arithmetic_operation.a -o main.o
// 혹은
clang++-9 make_library/cube.o make_library/main.o make_library/arithmetic_operation.a -o linking_main_cube_arithimetic.out
// 혹은
clang++ -o linking_main_cube_arithimetic.out main.o cube.o -Lpath/to/libarithmetic_operation.a -larithmetic_operation // 이때 확장자와 앞의 lib은 붙히지 않음.
|
자세한 파일 내용
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| // main.cpp
#include <cstdio>
int add(int a, int b);
int mul(int a, int b);
int sub(int a, int b);
int div(int a, int b);
int cube(int a);
int main()
{
int example_num = 1;
example_num = add(example_num,example_num); // 2 = 1 + 1
example_num = mul(example_num,example_num); // 4 = 2 * 2
example_num = sub(example_num, 1); // 3 = 4 - 1
example_num = div(example_num, 3); // 1 = 3 / 3
example_num = sub(example_num, 2); // -1 = 1 -2
example_num = cube(example_num); // -1 = -1 * -1 * -1
printf("%i", example_num);
//-1
return example_num;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
| // cube.cpp
#include "cube.hpp"
int cube(int a)
{
return a*a*a;
}
|
동적 라이브러리 $($shared library$)$
링킹 할 때 라이브러리를 링킹 할 수도 있고, 실행중에 메모리에 올려서 사용 할 수도 있다.
동적 라이브러리 만드는 방법
파일 구조
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| make_library/
├── Makefile
├── add.cpp
├── add.hpp
├── add_.o
├── div.cpp
├── div.hpp
├── div_.o
├── libarithmetic_operation.so // 만들어짐
├── main.cpp
├── main.o
├── mul.cpp
├── mul.hpp
├── mul_.o
├── sub.cpp
├── sub.hpp
└── sub_.o
|
shared Makefile
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| CC = clang++-9
flag = -c -fPIC -o # postion independent code
add_.o : add.cpp add.hpp
$(CC) $(flag) add_.o add.cpp
mul_.o : mul.cpp mul.hpp
$(CC) $(flag) mul_.o mul.cpp
sub_.o : sub.cpp sub.hpp
$(CC) $(flag) sub_.o sub.cpp
div_.o : div.cpp div.hpp
$(CC) $(flag) div_.o div.cpp
libarithmetic_operation.so : add_.o mul_.o sub_.o div_.o
clang++-9 -shared -o libarithmetic_operation.so add_.o mul_.o sub_.o div_.o
|
링킹하여 실행 하는 법
1
2
3
4
5
6
| clang++-9 -o print_-1.out main.o cube.o -L./ -larithmetic_operatio
// print_-1.out이 만들어짐!
./print_-1.out
error while loading shared libraries: libarithmetic_operation.so: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
//위와 같은 에러가 뜰 것이다.
|
호출할 라이브러리의 위치를 알아야 한다.
/etc/ld.so.conf 이 위치가 dll을 찾아보는 위치를 담고 있다.
혹은 환경변수 LD_LIBRARY_PATH를 활용하여 만들 수 있다.
1
| export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=~/desktop/c_cpp_compile_process/make_library
|
동적 라이브러리 살펴보는 방법
1
2
3
| ldd make_library/print_-1.out
// export 명령어 치기 전 결과 : libarithmetic_operation.so => not found
// export 명령어 친 후 결과 : libarithmetic_operation.so => /home/qhrqufdlek/desktop/c_cpp_compile_process/make_library/libarithmetic_operation.so
|
1
2
| # ln -s libmycalcso.so.1.0.1 libmycalcso.so
shared library를 symbolic link 하면, version constrol하기 쉽다. <br>
|
Execution time에 메모리에 올려 실행하는 방법
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| #include <dlfcn.h>
// 써야 하는 함수의 prototype
void *dlopen (const char *filename, int flag);
// 일반 명명규칙(lib*.so)을 따르지 않아도 되고, LD_LIBRARY_PATH 환경변수에 directory를 추가하지 않아도 된다.
// 오류 발생시 NULL이 return된다.
const char *dlerror(void);
void *dlsym(void *handle, const char *symbol);
// symbol(함수 또는 전역변수)의 위치에 대한 pointer를 얻습니다.
// handle : return 받은 shared object handle
// symbol : shared object에서 찾고자 하는 symbol
// return 함수를 찾는데 NULL이 return됐으면 error. 아니면 dlerror로 찾음.
|
dlfcn.h 라이브러리를 사용하는 파일은 -ldl로 컴파일 해야한다. libdl.so를 이용하기 때문이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| //run_time_linking.cpp
include <dlfcn.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int one = 1;
int result;
char *error;
int (*ptr_sum)(int, int) = NULL;
void *handle = dlopen ("/home/qhrqufdlek/desktop/c_cpp_compile_process/make_library/libarithmetic_operation.so", RTLD_LAZY);
if(handle == NULL)
{
printf("%s\n", dlerror());
return 1;
}
ptr_sum = (int (*)(int, int))dlsym(handle, "_Z3addii");
//아니 name mangling 된 것까지 symboltable 보고 가져와야 함?
printf("%s\n", dlerror());
if((error = dlerror()) != NULL)
{
printf("error\n");
dlclose(handle);
return 1;
}
printf("%i \n", ptr_sum(one, one));
dlclose(handle);
return 0;
}
|
1
2
| // command
clang++-9 -o runtime_linking.out -ldl runtime_link.cpp
|
!주의! dlsym$($handle, "_Z3addii"$)$에서 함수의 이름이 _Z3addii가 됐다.
이는 c++이 name mangling$($overloading, 같은 이름의 함수 사용하기 위해 함수 이름을 변환 시킴$)$ 때문이다.
1
2
3
| // 2가지 command로 해당 함수에 해당하는 symbol을 볼 수 있다.
nm libarithmetic_operation.so |grep add
readelf -a libarithmetic_operation.so
|
를 통해 so file 안의 symbol talbe에서 add 함수가 있는 곳을 알 수 있다.
혹은 shared library를 만들 때, extern “C” keyward를 활용하여, name mangling을 막아야 한다.
1
| extern "C" int test_dl_func();
|
출처
씹어 먹는 c++
embedded recipy
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/6561273/is-liblibrary-name-a-so-a-naming-convention-for-static-libraries-in-linux
https://www.joinc.co.kr/w/Site/C/Documents/CprogramingForLinuxEnv/Ch12_module
https://yaaam.tistory.com/entry/Linux-%EB%8F%99%EC%A0%81-%EB%9D%BC%EC%9D%B4%EB%B8%8C%EB%9F%AC%EB%A6%AC-%EB%A1%9C%EB%93%9C-dlopen-dlsym-dlclose-dlerror
https://modoocode.com/321
https://www.it-note.kr/186
https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man3/dlopen.3.html
https://umbum.dev/494
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/18096596/using-dlsym-in-c-without-extern-c
 위의 그림이 두 라이브러리의 차이를 잘 보여준다.
위의 그림이 두 라이브러리의 차이를 잘 보여준다.
Comments